A Disk on Which You Can Write Multiple Times Sometimes Is Called a _____ Disc.
What is a storage medium (storage media)?
In computers, a storage medium is a concrete device that receives and retains electronic data for applications and users and makes the data bachelor for retrieval. The storage medium might be within a estimator or other device or attached to a organisation externally, either direct or over a network. The plural course of this term is storage media.
Early forms of storage media included calculator paper tape with holes punched into information technology. Each pigsty corresponded to a single bit of data. A paper tape reader would translate the hole and convert information technology to a number. Punched cards were too widely used in the early days of data storage and at i fourth dimension stored nigh of the globe'due south digital information.
Paper tape and punched cards were supplanted past magnetic tape, which eventually gave way to magnetic floppy disks. Hard disk drives (HDDs) and solid-country drives (SSDs) are now the primary forms of storage.
How storage media works
Media used in computer storage receive messages in the form of data, via software commands from a host organisation. The blazon of media needed to concord the information depends on the information'southward business value, applicative compliance regulations, operation and availability requirements and other factors.
A storage medium may be internal to a computing device, such as a computer'south SSD, or a removable device such as an external HDD or universal serial bus (USB) flash drive. There are also other types of storage media, including magnetic tape, compact discs (CDs) and non-volatile memory (NVM) cards.
An organization's storage is oftentimes classified as chief and secondary. Originally, principal storage referred to data that is kept in memory for fast retrieval by a estimator's processor, and secondary storage referred to information stored on non-volatile devices such as SSDs and HDDs.
More recently, primary storage has come to refer to any type of retentivity that supports an arrangement's day-to-24-hour interval workloads. For case, the HDDs, SSDs or storage-form retentivity (SCM) devices that shop data for mission-critical applications are considered primary storage. In contrast, secondary storage tin can refer to only well-nigh anything else, including optical discs or tape systems that support long-term data retention.
In tiered storage, automated software policies are used to move data betwixt different storage types, such as HDDs, SSDs and cloud platforms.
The term storage medium can refer to a storage device in its entirety or to an individual component that's used in conjunction with or is part of another system. For example, the internal HDDs and SSDs in computers are commonly referred to as storage media, equally are CDs, but the CD drive itself is thought of as a storage device or system, rather than storage medium.
Similarly, an array is a complete storage organisation made up of private storage media. An assortment is frequently decoupled from the application server and attached to a separate server and accessed over a network. An array might be made upwards of HDDs or SSDs, or information technology might be ready upwards in a hybrid configuration that blends HDDs and SSDs into an integrated system, with HDDs providing a capacity tier that supports the faster SSDs.
Storage media can be arranged in multiple ways, depending on workload requirements. Some well-known configurations include:
- redundant array of independent disks (RAID);
- network-attached storage (NAS); and
- storage area network (SAN).
These configurations are not mutually exclusive. For case, a SAN often arranges storage into RAID configurations.
Different types of storage media
Storage media comes in many different forms, among them:
Hard disk drive drives
An HDD provides a high-capacity alternative to magnetic storage media such as tape or floppy disks. It contains metallic platters coated with a magnetic layer. The platters usually spin continuously when a computer is on, storing data in different sectors on the magnetic disk.
Difficult disks continue to be the dominant media for backup storage appliances, active archives and long-term retention. A disk-based fill-in appliance might as well include interfaces to replicate data copies, such as clones and snapshots, to tertiary devices or a hybrid cloud.
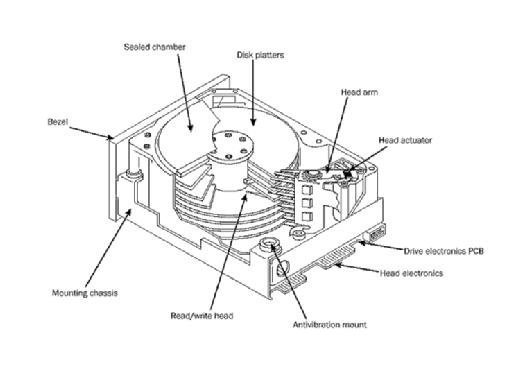
A downside to HDDs is the reliance on moving internal mechanisms such every bit actuators, motors and spindles that tin can fail and corrupt the drive. However, HDDs remain popular in enterprise disk arrays due to their increasing capacities and the ability to rewrite data on the deejay. In 2017, Western Digital Corp. introduced a 14 TB HDD, making it the largest on the market at that time. Seagate Applied science followed in 2022 with a xvi TB HDD. Western Digital has since countered with a 20 TB HDD.
Some HDDs use shingled magnetic recording (SMR) every bit an alternative to conventional magnetic recording. An SMR method allows for greater areal density by allowing data to be written in partially overlapping tracks on the disk. SMR drives piece of work optimally with data that is continuously written, such as disk-based archiving and fill-in, but it tin negatively affect performance for other types of workloads.
Seagate, Western Digital and Toshiba are amidst the leading manufacturers of SMR-based disks. In 2020, however, controversy surrounded the three vendors for allegedly selling HDDs without disclosing they used SMR technology.
RAID
RAID works by placing data on multiple disks and balancing input/output (I/O) operations across those disks. RAID can improve performance, fault tolerance or both, depending on the RAID configuration. If RAID is gear up for fault tolerance, the information is protected in the event a drive fails. The use of multiple disks besides increases the mean fourth dimension between failures (MTBF).

Flash memory
Flash memory does not depend on moving mechanical parts. Instead, data is written to microchips, making storage operations much faster than traditional disks. Yet, data must be erased and rewritten in entire blocks, which can bear upon a device's overall endurance.
At that place are two primary types of flash SSDs: NAND and NOR. The names are divers by their respective logic gates, which determine the fundamental architecture underlying digital circuits.
NAND flash memory is written and read in blocks, whereas NOR flash memory reads and writes bytes independently. Both types of flash are used in a broad range of devices. NOR flash tends to exist used in embedded systems that support devices such as medical equipment and scientific instruments, every bit well as consumer devices such as tablets and smartphones. In some cases, NOR serves equally a replacement for random access memory (RAM) or read-only memory (ROM) drives.
NAND flash is used for all types of general storage considering information technology is much more efficient at writes, erases and sequential reads. NAND flash is also known for college density and endurance than NOR, making it suitable for enterprise storage. Some devices use both types of flash. For example, a smartphone might rely on NOR to boot upward the operating system (OS) and NAND flash for all other storage.
SSDs based on NAND flash are oft categorized by the number of bits supported by each flash cell. Unmarried-level cell (SLC) NAND stores 1 bit of information per wink prison cell, which is in either a programmed (0) state or erased (i) state. Multi-level cell (MLC) NAND stores two bits of data per wink cell, triple-level cell (TLC) stores iii data bits per cell, and quad-level cell (QLC) stores four bits. Manufacturers are currently working on penta-level cell (PLC) wink, which squeezes 5 $.25 into each jail cell.
Flash storage memory devices are divided between consumer devices and enterprise storage, with some overlap. Enhancements are congenital into enterprise NAND flash devices to support more write cycles than consumer-grade storage. Smartphones, tablets and other consumer devices use retentiveness cards that vary in capacity and cost.
SSD
Organizations now use flash-based SSDs extensively for both network-based storage -- such equally NAS and SAN -- and direct-attached storage (DAS), which can be attached externally to a computer or embedded directly inside the system. Direct-attached SSDs are sometimes used as an alternative or adjunct to networked storage arrays.
Internal SSDs come in a number of form factors, including:
- add together-in cards that employ a Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe) serial port;
- disk-on-module (DOM) flash kick drives that mount to a computer's motherboard;
- wink-based dual inline memory modules (DIMMs) that sit down in dynamic random-admission memory (DRAM) slots on the motherboard to provide a operation cache;
- miniSATA (mSATA) drives and their eventual replacement, 2 SSDs, which are used in thin laptops; and
- storage-form memory, which combines DRAM and NAND to provide non-volatile retentiveness that runs in the server'due south retentivity space (3D XPoint engineering science -- adult by Intel and Micron -- is an instance of storage-class memory).
SSDs initially were designed to take advantage of existing Serial-Fastened SCSI (SAS) and Serial-Advanced Engineering science Zipper (SATA) protocols, only many SSDs now use the non-volatile memory express (NVMe) protocol considering it tin take improve reward of SSD capabilities.

NVMe uses a computer's PCIe ports to enable an application to communicate directly with a data storage device. PCIe-based NVMe SSDs aim to reduce latency and boost throughput. The success of NVMe led to the evolution of non-volatile retentivity express over fabrics (NVMe-oF). NVMe-oF makes it possible to use NVMe commands to transfer data between a host and flash storage device across an Ethernet, Fibre Aqueduct or InfiniBand connection.
USB wink drives
A USB flash bulldoze is a type of removable storage medium that attaches to a server or other device through a USB port. A USB wink drive seldom connects continuously to a device, which tin make it less susceptible to Trojan horses, viruses or worms.
The term USB wink drive refers to the device in its entirety, including the USB connector, whereas the storage medium is the internal flash scrap. USB flash drives can vary in size, simply they're generally near the size of a thumb, with a design similar to SSDs but on a smaller scale. USB flash drives attach to devices by sliding into compatible USB ports, making it possible to chop-chop transfer or re-create data. The drives are variously chosen memory sticks, keychain drives, pollex drives and leap drives.

Although USB drives are widely used past consumers due to their convenience, that ease of use can present a security risk for enterprises. For security reasons, many companies foreclose employees from using personal USB drives at work, unless specifically authorized to do so.
Other removable flash storage media include the Secure Digital carte (SD menu), microSD card, Secure Digital High Capacity card (SDHC carte), CompactFlash card, SmartMedia card, Sony Retention Stick, MultiMediaCard (MMC) and the xD-Picture show Bill of fare, all of which are found mainly in consumer electronics.
Optical disc
Optical disc technology uses lasers to write and read information. Many optical discs support write once, read many (WORM) operations only. When first introduced, optical discs could store more information than magnetic HDDs, just that has since changed, and optical discs are now used primarily for prerecorded audio and video recordings or for fill-in and archival purposes. Types of optical storage media include Blu-ray discs, DVDs, CDs and CD-ROMs (for read-but information).

Record
Record was a ascendant backup storage medium until the 1990s but was gradually pushed aside past magnetic deejay. Even and then, tape systems are still often used for loftier-chapters information archiving and take connected to meliorate in density and endurance, largely due to advances in the Linear Tape-Open (LTO) format. LTO-9 pushes the per-tape chapters to 45 TB of compressed data and eighteen TB of native (uncompressed) information.
Record libraries are composed of hundreds and hundreds of concrete tapes. The system that supports a record library enables users to add or remove tapes, rails a record's location and set mount points for accessing the information on tape.

Some organizations are turning to virtual tape library systems for backup. In this type of system, an assortment of physical disks is presented as record to the fill-in software. Information is written sequentially as information technology is with record, but read and write operations are faster considering the information is retrieved from magnetic disks.
Source: https://www.techtarget.com/searchstorage/definition/storage-medium
Belum ada Komentar untuk "A Disk on Which You Can Write Multiple Times Sometimes Is Called a _____ Disc."
Posting Komentar